
In today's tech-savvy world, the functionality of electronic devices is crucial, and one essential component that often goes unnoticed is the membrane switch. These thin, flexible, and durable switches play a significant role in various electronic applications, including control panels, medical devices, and industrial machinery. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the world of membrane switches, exploring their construction, operation, and applications in detail.
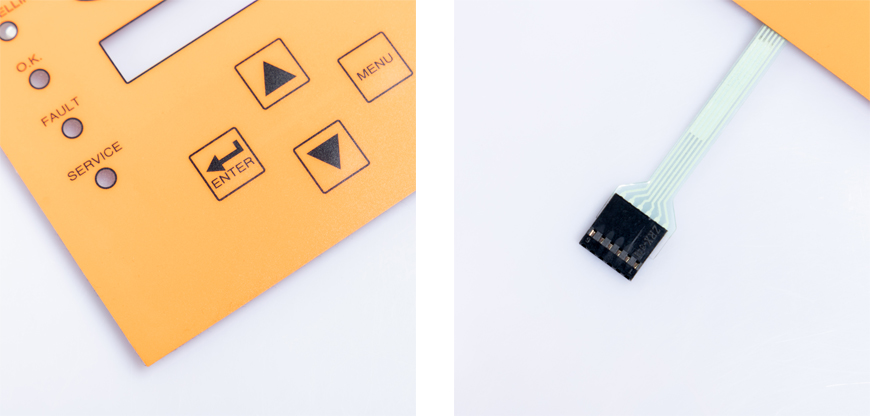
A membrane switch is a user interface that combines functionality with aesthetic appeal. These switches are composed of multiple layers of flexible materials that work together to perform various functions. Membrane switches are designed to be thin, compact, and durable, making them ideal for applications where space is limited and reliable operation is crucial. Their versatility has led to widespread adoption in consumer electronics, medical devices, industrial control panels, and more.
The top layer of a membrane switch is called the graphic overlay. It is the part of the switch that the user directly interacts with. This layer typically features printed graphics, icons, labels, and buttons that indicate the functions of the switch. The graphic overlay is often made from durable materials such as polyester, polycarbonate, or acrylic to ensure longevity and protection against wear and tear. The design of this layer is customizable to fit specific product requirements, such as colors, symbols, and user preferences.
Beneath the graphic overlay is the spacer layer, which separates the top and bottom layers of the membrane switch. The spacer is typically a non-conductive material that prevents the circuit from completing until pressure is applied. The spacer ensures the switch remains open until activated, providing a reliable and responsive user interface.
The bottom layer, also known as the circuit layer, contains the conductive traces that form the switch's circuit. This layer is typically made from materials like copper or conductive ink and is printed or etched onto a flexible substrate. When pressure is applied to the graphic overlay, the conductive traces make contact with each other, completing the circuit and triggering the desired function. The flexibility of the circuit layer allows the membrane switch to be lightweight and adaptable for different device applications.
To hold all the layers securely together, an adhesive layer is applied to the membrane switch. This layer ensures that the different components are firmly attached and remain intact, even in demanding environments. The adhesive used is typically a strong, pressure-sensitive type, which provides a strong bond without causing damage to the device surface during application.
Membrane switches such as led backlight membrane switch operate on the principle of pressure-sensitive contact. When a user applies pressure to a specific area on the graphic overlay, the flexible membrane layer bends and makes contact with the circuit layer beneath it. This action closes the electrical circuit, allowing current to flow and completing the input.
The membrane switch can be designed to provide feedback in two ways:
Tactile Feedback: Some membrane switches are designed with tactile feedback, providing a physical "click" or resistance when the switch is activated. This feedback helps users know when the input has been registered.
Non-Tactile Feedback: In other cases, membrane switches may not offer physical feedback but still respond reliably when pressure is applied, commonly used in sleek, minimalistic designs.
Membrane switches are designed to be both intuitive and reliable, with their simple, low-profile design offering easy integration into a wide range of devices.
Space-Saving Design: Membrane switches are thin and compact, making them ideal for use in devices where space is limited, such as consumer electronics, medical devices, and industrial control panels.
Durability and Longevity: Made from flexible materials, membrane switches are highly durable, resistant to wear, and capable of withstanding frequent use over long periods. They are less likely to break down compared to traditional mechanical switches.
Customization Options: Membrane switches are highly customizable in terms of design, layout, and function. Graphic overlays can be printed with custom symbols, logos, and color schemes to suit a brand's identity or user preferences. Additionally, membrane switches can be adapted for tactile or non-tactile feedback, depending on the application.
Resistance to Moisture and Contaminants: Because of their sealed construction, membrane switches are highly resistant to moisture, dust, dirt, and other contaminants. This makes them suitable for use in harsh environments, including industrial and medical applications.
Choosing the right materials is crucial for the performance and durability of the membrane switch. Materials such as polyester, polyimide, and polycarbonate are selected for the graphic overlay and the adhesive layers due to their flexibility, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. The conductive traces are often made from copper, silver, or conductive inks.
The graphic overlays are printed using specialized printing techniques, such as screen printing or digital printing, to ensure that the colors, text, and icons are accurate and durable. Once the graphic overlay is printed, it is carefully cut to the required shape and size to match the design specifications.
After the individual layers are prepared, they are carefully assembled. The spacer layer is placed between the graphic overlay and the circuit layer, ensuring that the switch remains open until activated. The layers are then bonded together with an adhesive layer, which is applied to secure all components in place. Connections are made to the circuit, and the switch is tested to ensure it functions correctly.
Before the membrane switch is shipped, it undergoes rigorous testing to ensure reliability. This includes tests for conductivity, pressure sensitivity, tactile feedback, and environmental resistance. Any potential issues are identified and resolved during this stage to ensure that the final product meets the necessary quality standards.
Q: Can membrane switches be used in outdoor applications?
A: Yes, membrane switches can be designed to be resistant to environmental factors, making them suitable for outdoor use.
Q: Are membrane switches easy to clean?
A: Yes, membrane switches are easy to clean and can withstand disinfection procedures, making them ideal for medical and industrial settings.
Q: What is the lifespan of a typical membrane switch?
A: The lifespan of a membrane switch can vary depending on usage, but they are known for their durability and can last for many years.
Q: Can I get a membrane switch with custom graphics?
A: Absolutely, membrane switches can be customized with graphics, icons, and labels to match the branding of your product.
Q: Are membrane switches cost-effective compared to mechanical switches?
A: Yes, membrane switches are often more cost-effective due to their lower production and assembly costs.