
In today's fast-paced technological world, membrane switches have become an integral part of many electronic devices. These switches are known for their versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. However, when it comes to designing and integrating them into various applications, one crucial aspect to consider is their weight. In this article, we will delve into the topic of how much membrane switches weigh, exploring the factors that influence their weight and providing valuable insights for manufacturers and users alike.
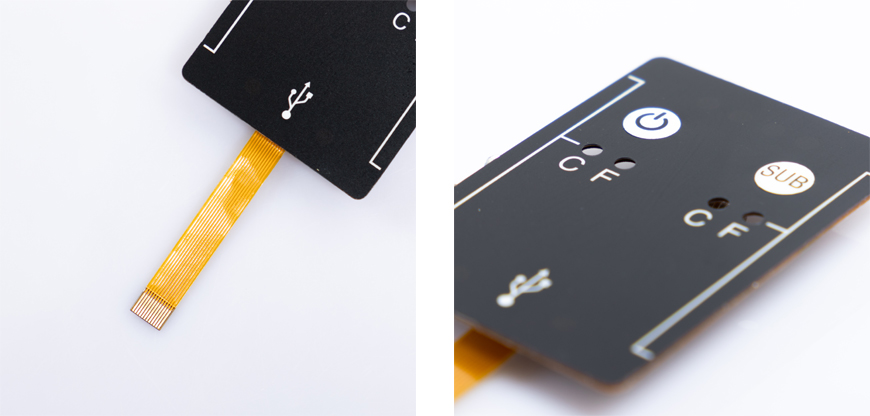
1. Introduction to Membrane Switches
2. The Construction of Membrane Switches
3. Factors Affecting Membrane Switch Weight
· Materials Used
· Number of Layers
· Size and Dimensions
4. Average Weight of Membrane Switches
5. Lightweight Membrane Switch Alternatives
6. Applications and Use Cases
7. Design Considerations
8. Installation and Maintenance
9. Membrane Switch Weight and Cost
10. Future Trends in Membrane Switch Technology
11. Conclusion
12. Frequently Asked Questions
Membrane switches are low-profile, user-interface technology used to communicate commands from users to electronic devices. They consist of multiple layers of flexible materials, including a graphic overlay, adhesive spacer, and conductive circuit. These switches offer a reliable and cost-effective solution for industries such as medical devices, aerospace, industrial equipment, and consumer electronics.
To understand the weight of membrane switches, it's essential to comprehend their construction. Membrane switches typically consist of three main layers: the top graphic overlay, the middle spacer layer, and the bottom circuit layer. The materials used in each of these layers can vary, influencing the overall weight of the switch.
Materials Used
The choice of materials plays a significant role in determining the weight of a membrane switch. While the graphic overlay is often made of polyester or polycarbonate, the spacer layer and circuit layer can be constructed from various materials, including polyester, polyimide, or even silicone rubber. Each material has its specific weight, affecting the overall switch weight.
Number of Layers
The number of layers in a membrane switch can vary depending on the complexity of the application and the desired functionality. Additional layers, such as tactile feedback layers or shielding layers, can add to the overall weight of the switch.
Size and Dimensions
The size and dimensions of a membrane switch also influence its weight. Larger switches with more extensive graphic overlays and circuitry will naturally weigh more than smaller counterparts.
On average, a standard membrane switch typically weighs between 5 to 30 grams. However, this range can vary significantly based on the factors mentioned earlier. Manufacturers can customize membrane switches to meet specific weight requirements for their applications.
For applications where weight is a critical concern, manufacturers can explore lightweight alternatives. Thin-film membrane switches and capacitive touch switches are examples of such alternatives, offering reduced weight without compromising functionality.
Membrane switches find applications in various industries, including:
· Medical devices, where hygiene and durability are essential.
· Aerospace, for control panels and cockpit instruments.
· Industrial equipment, for rugged and reliable user interfaces.
· Consumer electronics, for keypads and control surfaces.
Designers must consider weight as a factor when creating membrane switch interfaces. The choice of materials, number of layers, and overall dimensions should align with the intended use and weight restrictions of the device.
Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial to ensuring the long-term performance of membrane switches. Users should follow manufacturer guidelines to prevent damage or wear and tear that could affect the switch's weight and functionality.
While weight is a consideration in membrane switch design, it is often balanced with cost considerations. Heavier switches may cost more due to the materials used, but they may be necessary for specific applications.
As technology evolves, so does the design and manufacturing of membrane switches. Future trends may focus on reducing weight even further while maintaining durability and functionality.
In conclusion, the weight of membrane switches varies depending on factors such as materials used, the number of layers, and dimensions. Designers and manufacturers should carefully consider these factors to meet the specific requirements of their applications. Membrane switches continue to be a valuable solution in various industries, offering reliable and cost-effective user interfaces.
Are membrane switches durable?
Yes, membrane switches are known for their durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Can I customize the weight of a membrane switch?
Yes, manufacturers can customize membrane switches to meet specific weight requirements.
What industries commonly use membrane switches?
Medical devices, aerospace, industrial equipment, and consumer electronics are common industries using membrane switches.
Are lightweight membrane switch alternatives as durable as standard switches?
Lightweight alternatives can be durable, but the choice depends on the specific application's requirements.
What is the future of membrane switch technology?
The future may involve even lighter and more advanced membrane switch designs to meet evolving industry needs.